Welding is a hazardous activity, which is why it is important to understand the intricacies involved in the process. Choosing the right type of welding machine and accessories is important to reduce the risk involved. This isn’t just for getting the job done, but it allows the welder to do the task efficiently, effectively, and most of all —safely.
The type of welding machine plays a crucial role in the overall safety and quality of welding work. The correct machine ensures clean, precise welds, reduces accidents, and improves project efficiency. In this article, we will help you navigate through the various types of welding machines, their applications, and the essential features you need to prioritize for safety and longevity.

Common Welding Machines and Their Applications
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each welding machine ensures better project outcomes and efficiency in industrial, automotive, or creative applications. Below is a list of welder machine types and their applications.
1. MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding
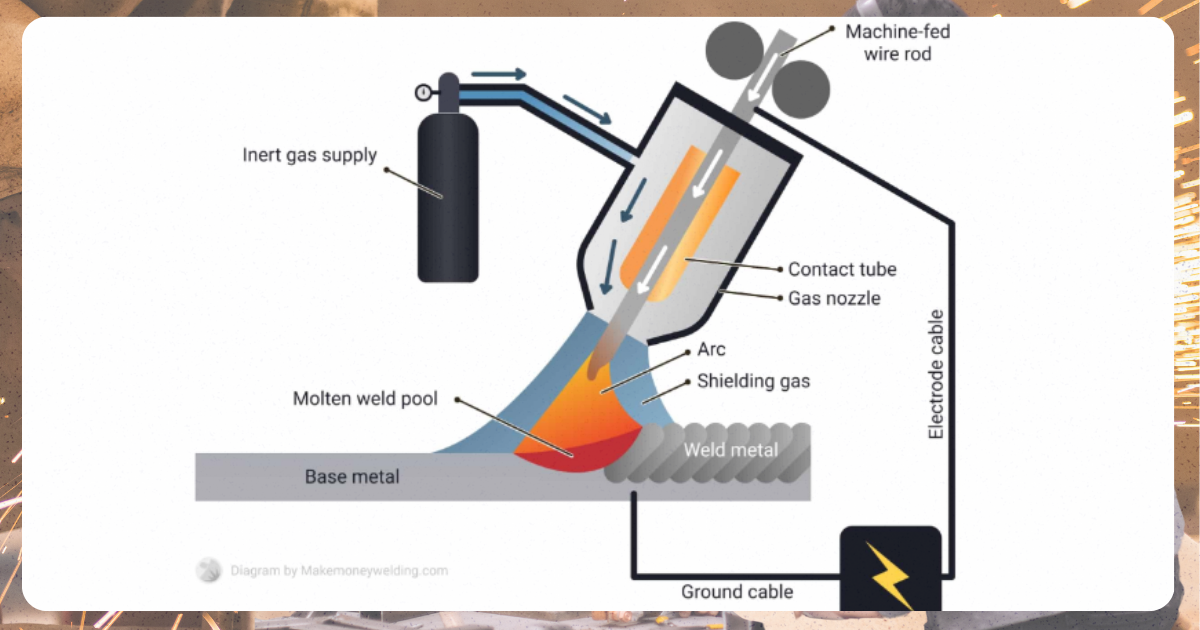
Image from MakeMoneyWelding
MIG welding is a commonly used welding technique. The welding gun continuously feeds a consumable wire electrode, creating a stable arc.
This type is perfect for materials like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Automotive, construction, and robotics widely use it, especially for large, thick materials that require consistent welds.
There are subtypes of MIG welding machines, namely:
- Basic MIG welders: mostly used for light-duty welding projects.
- Multi-process welders: used for heavy-duty welding projects.
- Pulse MIG welders: used for high-quality, precision welding projects.
2. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding
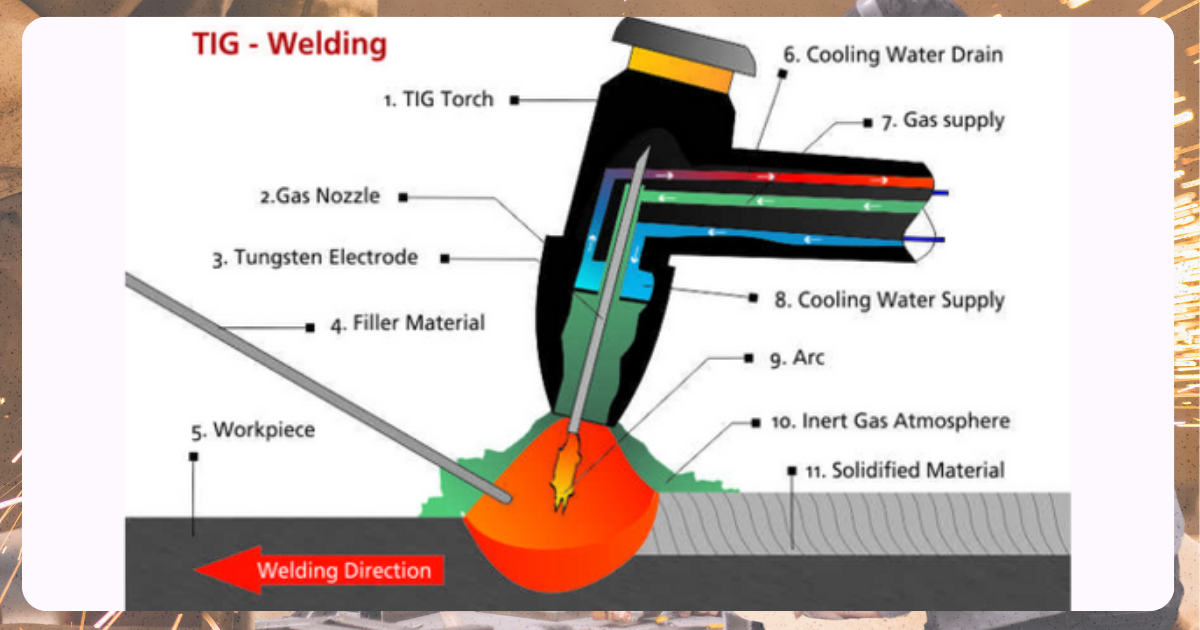
TIG welding is known for its precision. It requires the welder to handle a tungsten electrode and filler wire to join metals.
TIG is perfect for thin metals, such as aluminum, titanium, and magnesium, making it a favorite for aerospace, race car fabrication, and artistic applications. This method offers exceptional control but requires more skill and concentration than MIG welding.
3. Stick/SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding)
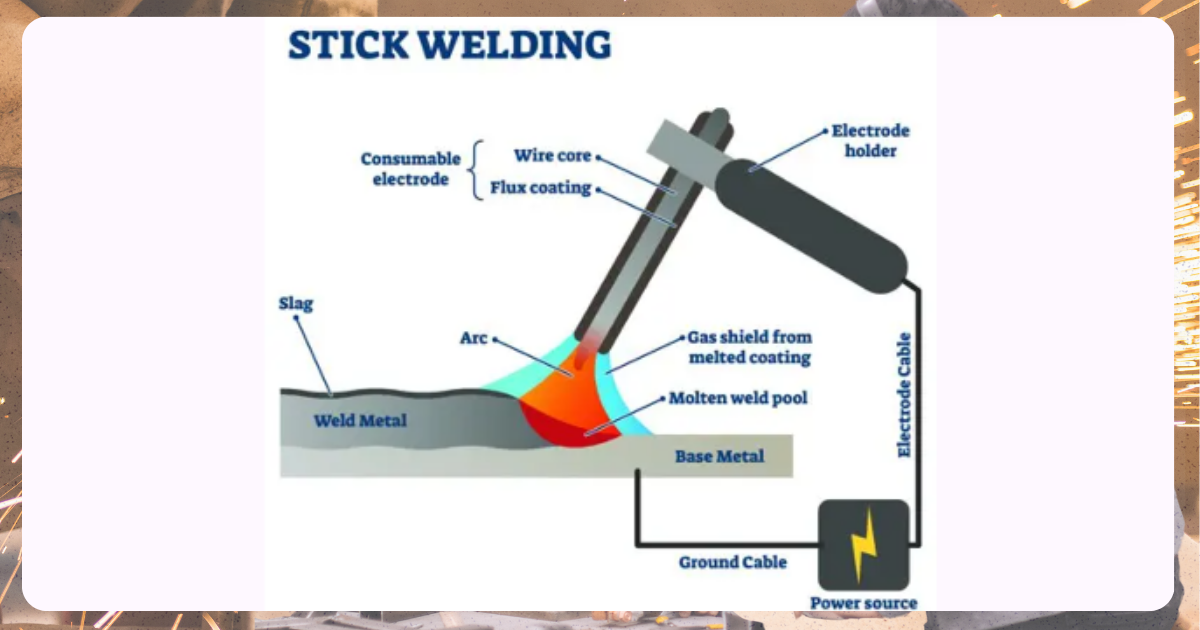
Image from Fractory
Stick welding is versatile and widely used in various environments, especially outdoor work. It uses a flux-coated electrode, which provides a stable arc and helps shield the molten weld pool.
Ideal for steel, stainless steel, and cast iron, stick welding is common in pipeline welding and equipment repairs, thanks to its ability to handle rough conditions and a wide range of materials.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
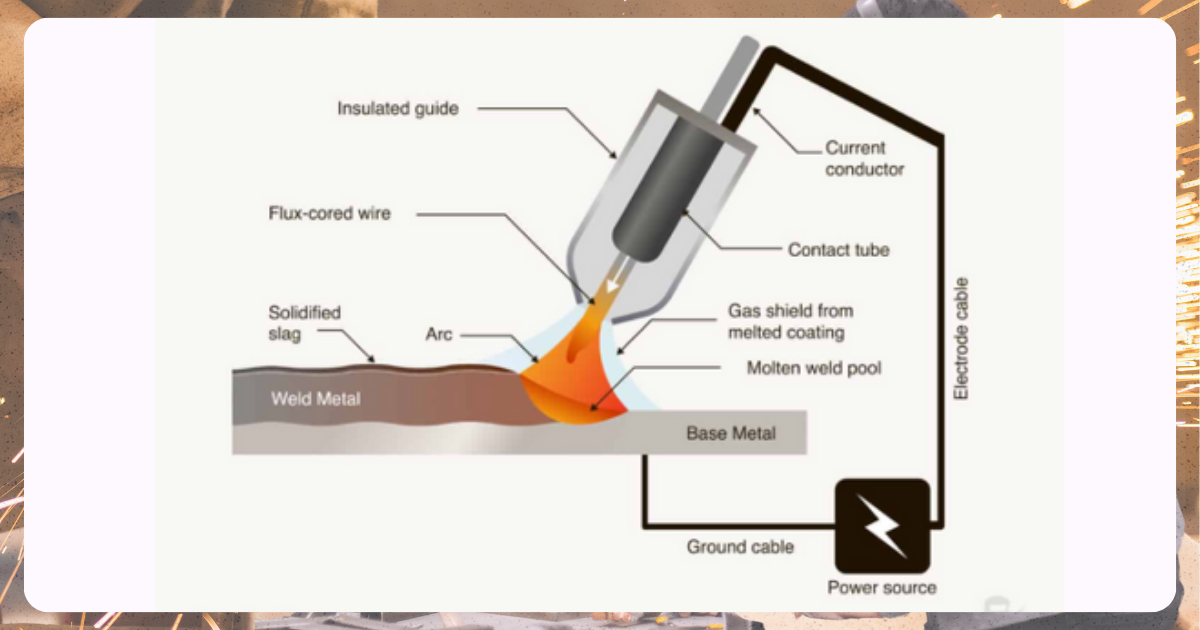
Image from Weld Guru
Similar to MIG welding, Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) uses a tubular wire filled with flux that shields the arc. This process doesn’t require external shielding gas, making it ideal for outdoor conditions. Construction, fabrication, and high-heat applications use it best for thicker metals.
Other Welding Machines for Specialized Applications
- Energy Beam Welding (EBW): EBW uses focused electron beams in a vacuum to melt and join metals. The aerospace, automotive, and medical industries mostly employ it when accuracy is crucial.
- Plasma Arc Welding (PAW): Plasma Arc Welding offers laser-like precision, making it perfect for delicate industrial applications such as aircraft manufacturing. However, it comes at a higher cost compared to other methods.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): This automated or semi-automated process uses a continuous wire electrode and a flux that completely submerges the arc. Heavy-duty applications like pipeline construction and pressure vessels, which prioritize high efficiency and large-scale operations, primarily use it.
- Atomic Hydrogen Welding (AHW): AHW combines tungsten electrodes and hydrogen shielding gas to create a stable arc. Newer technologies are increasingly replacing it, despite its suitability for both thin and thick materials.
- Oxyacetylene Gas Welding: Oxyacetylene welding uses a flame from an oxygen-acetylene mix to melt and join metals. It’s portable, making it ideal for light fabrication and repairs, particularly in automotive work.
- Multi-Process Welding Machines: These versatile machines can perform multiple welding processes—such as MIG, TIG, and Stick—within one unit. This makes them ideal for welders who need to switch between methods depending on the materials and job requirements.
Key Safety Features to Look For In A Welding Machine
Understanding the essential safety features of a welding machine guarantees protection against potential risks like overheating, electrical overloads, and arc flashes. Features like automatic shut-off and stable arc technology help maintain safe and efficient operation, reducing the risk of accidents. Choosing machines with these safety features protects your health and makes your equipment last longer.
When choosing a welding machine, safety features should be a top priority.
1. Automatic Shut-off
The machine automatically shuts off when it reaches unsafe levels, a critical safety feature that prevents overheating and fire hazards.
2. Overload Protection
It shields the machine and the user from electrical overloads, which lowers the danger of accidents and prolongs the equipment’s lifespan.
3. Stable Arc
It guarantees steady welds with little variation, shielding the welder from sparks or arc flashes that could injure them.
4. Compatibility with Safety Gear
Make sure the machine works seamlessly with necessary safety gear, such as welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing, to ensure full protection during operation.
Maintenance Tips to Ensure Your Safety and Longevity of The Machine

Of course, a well-maintained machine will perform better for longer while keeping you safe on the job. Below are some important safety and maintenance tips that you can follow to keep your welding machine in top shape for longer:
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Cleaning and inspecting the welding machine regularly can prevent malfunctions. This includes checking the cables, electrodes, and cooling systems.
- Ensure Proper Storage: Store your welding machine in a dry, secure area to protect it from environmental factors that can cause damage, such as rust or dirt buildup.
- Check for Wear and Tear Periodically: Schedule the inspection of key components like cables, connectors, and safety switches to ensure they are in excellent working condition. Worn parts can compromise both safety and functionality.
- Routine Maintenance: Ensure that the cooling system is functioning properly and make sure to replace worn-out parts if necessary. Regular maintenance will help avoid malfunctions during operation and extend the life of your equipment.
Arc Your Way to Safety
Choosing the right welding machine is essential for ensuring a safe and efficient work environment. It’s important to assess your project requirements, the materials you’re working with, and the necessary safety features before making a decision.
Regular maintenance is equally important for keeping your machine in optimal condition. Assess your current equipment and consider upgrading parts or performing regular maintenance to enhance your safety and the performance of the machine.
Safe and efficient welding starts with the right machine, ka-Builders!
References:
Eziil. (n.d.). Guide to Welding Machine Types and Their Applications. Eziil. Retrieved November 20, 2024, from https://eziil.com/welding-machine-types/
Meg-Meet.com. (2023, August 14). 10 Common Welding Machine Types and Their Applications. Meg-Meet.com. Retrieved November 20, 2024, from https://www.megmeet-welding.com/en/news/10-Welding-Machine-Types-and-Their-Applications
SafetyCulture. (2024, October 2). Welding Safety: Hazards, Tips, & Precautions. SafetyCulture. Retrieved November 20, 2024, from https://safetyculture.com/topics/welding-safety/










