Circuit breakers and fuses play a critical role in ensuring the safety and functionality of modern electrical systems. A circuit breaker functions as a safety device, automatically interrupting the flow of electricity during faults, while fuses accomplish the same task by melting a wire to break the circuit. Both devices are essential for preventing overloads and electrical fires, making them important components of any infrastructure.
Understanding how circuit breakers and fuses operate is important not only for construction and electrical professionals but also for homeowners and DIY renovators looking to enhance the electrical safety of their homes. This article provides a comprehensive guide to various types of circuit breakers, their related symbols, and practical applications, empowering readers to make informed decisions about their electrical systems.

Understanding Circuit Breakers and Fuses
Circuit breakers and fuses serve important purposes in protecting electrical circuits from damage in case of overload or faults. A circuit breaker automatically interrupts the flow of electricity in case of any unprecedented issue, and a fuse acts as a sacrificial device that melts and breaks the circuit when an overload occurs.
While both devices safeguard electrical systems, circuit breakers allow for reset and reuse, while fuses necessitate replacement after use. Selecting the appropriate circuit breaker or fuse is essential to ensure adequate protection and functionality in various applications.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Knowing the types of circuit breakers is important when selecting the best protection for your electrical systems. Each type of circuit breaker serves a specific purpose, such as preventing overloads, detecting ground faults, or protecting electrical systems against short circuits.
Understanding these differences can help prevent electrical hazards, reduce the risk of damage to your equipment, and enhance overall system reliability. Below are the types of circuit breakers, their functions, and applications.
1. Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Function: Protects against overloads.
- Application: Residential and light commercial.
2. Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Function: Protects against overloads and short circuits.
- Application: Industrial and commercial settings.
3. Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB/RCD)
- Function: Detects ground faults.
- Application: Protecting people from electric shock.
4. Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
- Function: Detects earth faults.
- Application: Older systems where ground fault protection is needed.
5. Residual Current Breaker with Overload (RCBO)
- Function: Combines features of RCCB and MCB.
- Application: Comprehensive protection in residential settings.
6. Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
- Function: Prevents electrical fires caused by arcing faults.
- Application: Living areas and bedrooms.
7. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
- Function: Protects against ground faults in wet areas.
- Application: Bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor circuits.
8. Direct Current Circuit Breaker (DC CB)
- Function: Designed for DC systems.
- Application: Solar power systems and battery applications.
9. Wi-Fi Circuit Breaker (WiFi CB)
- Function: Smart breakers with connectivity features.
- Application: Smart homes and energy management systems.
10. Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
- Function: Suitable for high-voltage applications.
- Application: Large commercial and industrial settings.
11. Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB)
- Function: Uses a vacuum to extinguish the arc.
- Application: Medium voltage applications.
12. Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB)
- Function: Protects motors from overloads and short circuits.
- Application: Motor control systems.
13. Sulfur Hexafluoride Circuit Breaker (SF6 CB)
- Function: High-voltage applications using SF6 gas.
- Application: Power distribution and substations.
14. Mechanically Operated Circuit Breaker (MOCB)
- Function: Manual or automated operation.
- Application: Various industrial applications.
15. Bimetallic Overcurrent Circuit Breaker (BOCB)
- Function: Overcurrent protection using bimetallic strips.
- Application: Household and commercial appliances.
16. Automotive Circuit Breaker
- Function: Protects automotive electrical systems.
- Application: Cars and recreational vehicles.
17. High Voltage Direct Current Circuit (HVDC) Circuit Breaker
- Function: Controls high-voltage direct current systems.
- Application: Power transmission systems.
Circuit Breaker Symbols & Their Meanings
Circuit breaker symbols can be considered a universal language for identifying different types of breakers and their functions. Understanding these symbols helps in the proper interpretation of electrical diagrams and schematics, ensuring accurate installation and maintenance. Below are circuit breaker symbols and their meanings.
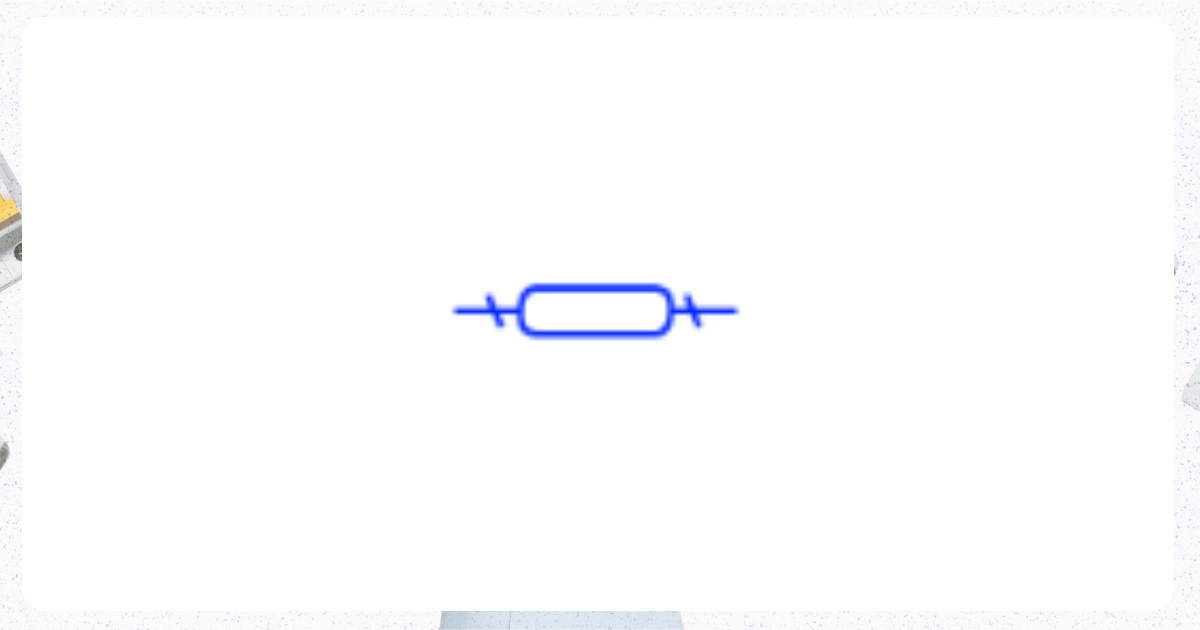
1. Breaker
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
A protective device, commonly known as a general term, automatically halts the flow of electricity in a circuit upon detecting a fault, thereby averting damage to electrical systems and mitigating the risk of fire.
2. Non Draw Out Circuit Breaker
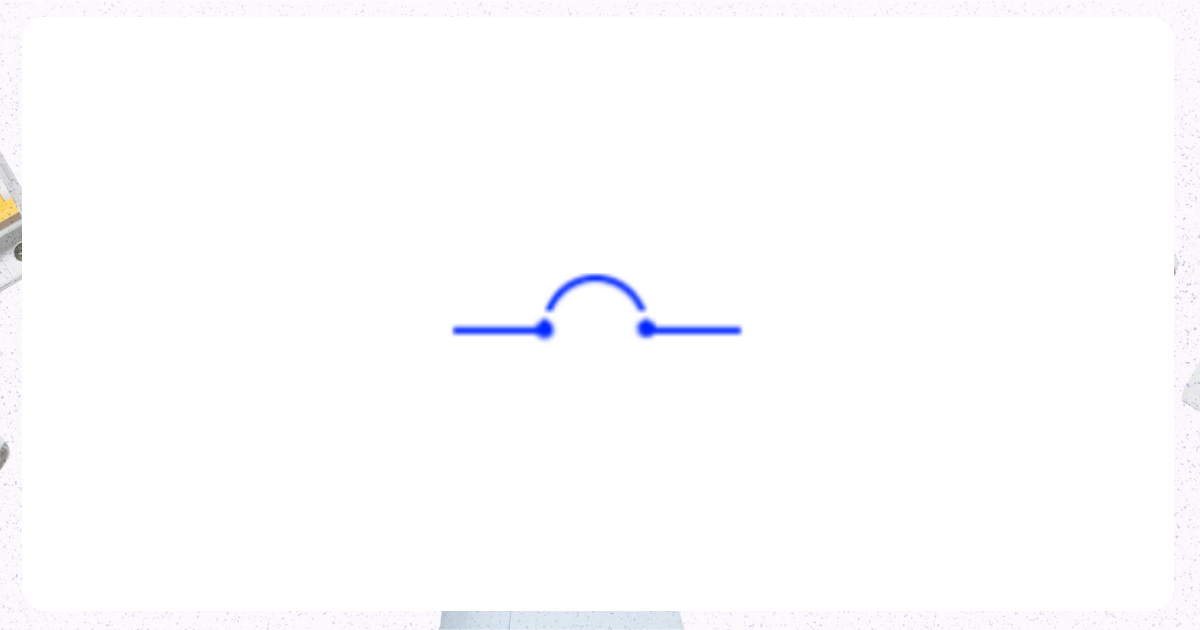
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
This type of circuit breaker is fixed and cannot be removed from its panel or housing for maintenance or replacement.
3. Draw Out Circuit Breaker
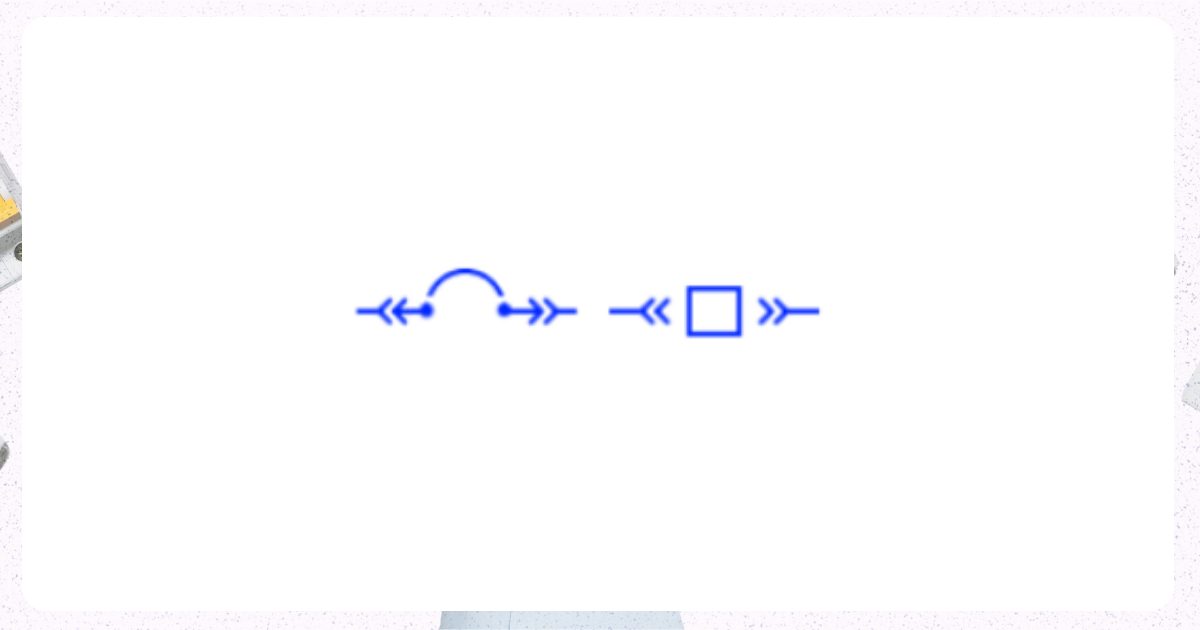
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
A circuit breaker that can be easily removed from its housing or panel for maintenance or replacement.
4. Threaded Circuit Breaker
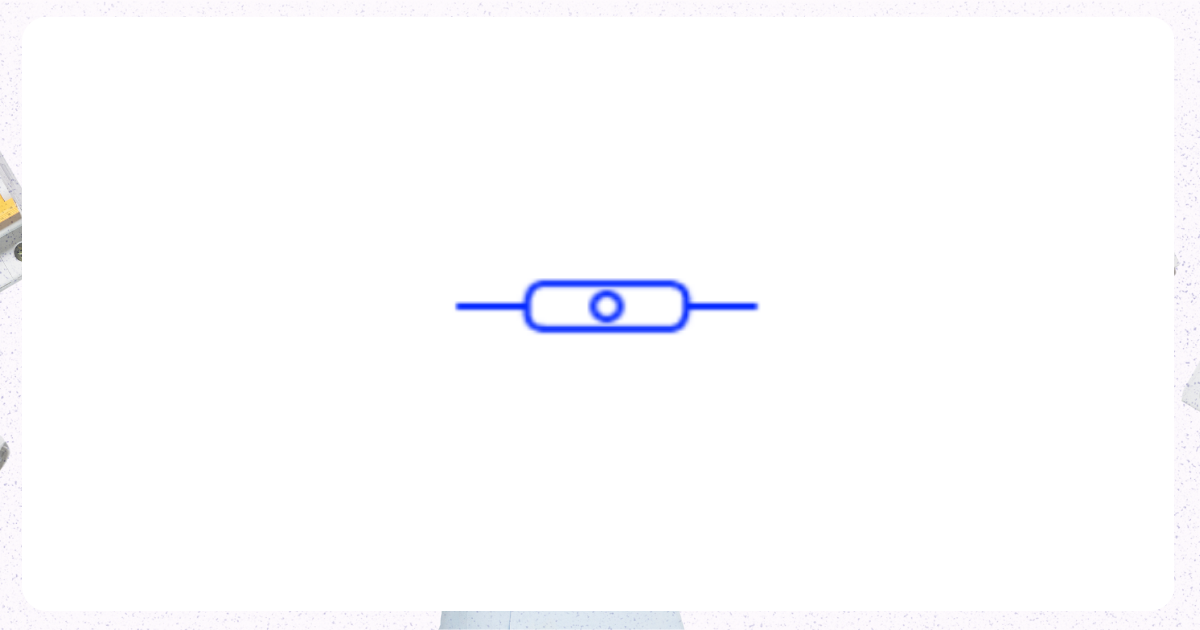
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
Threaded connections secure this type of circuit breaker in place, ensuring a secure and robust installation for areas handling or storing hazardous materials.
5. Single Pole Circuit Breaker
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
A circuit breaker that protects a single electrical circuit.
6. Double Pole Circuit Breaker
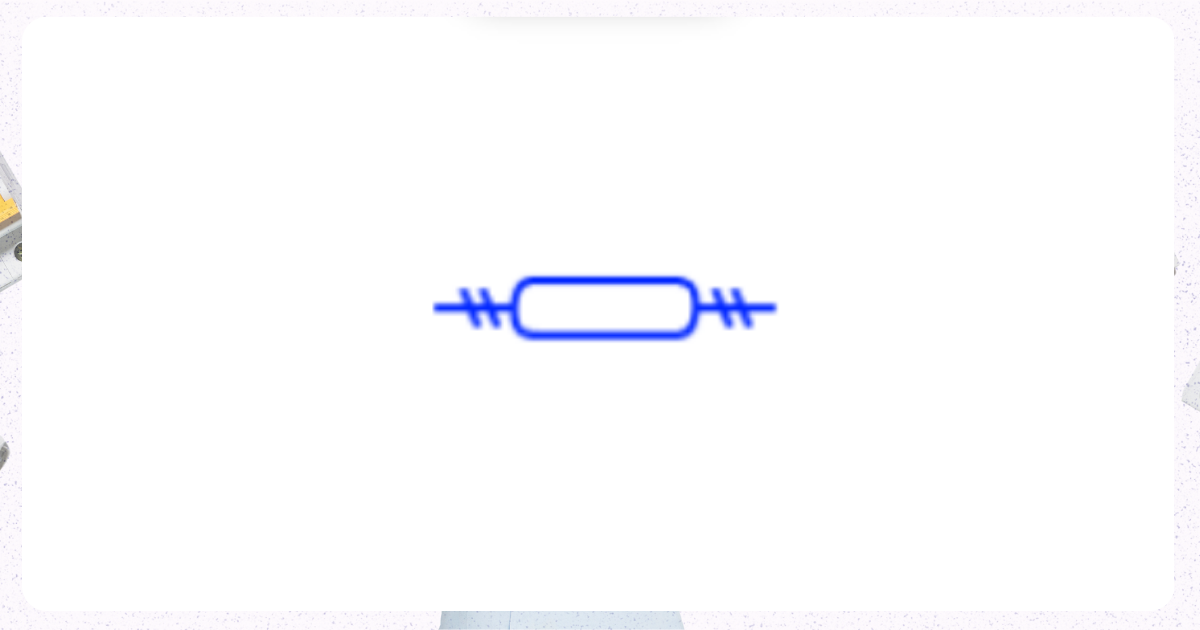
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
This breaker connects to two circuits, providing protection for both.
7. Three Pole Circuit Breaker
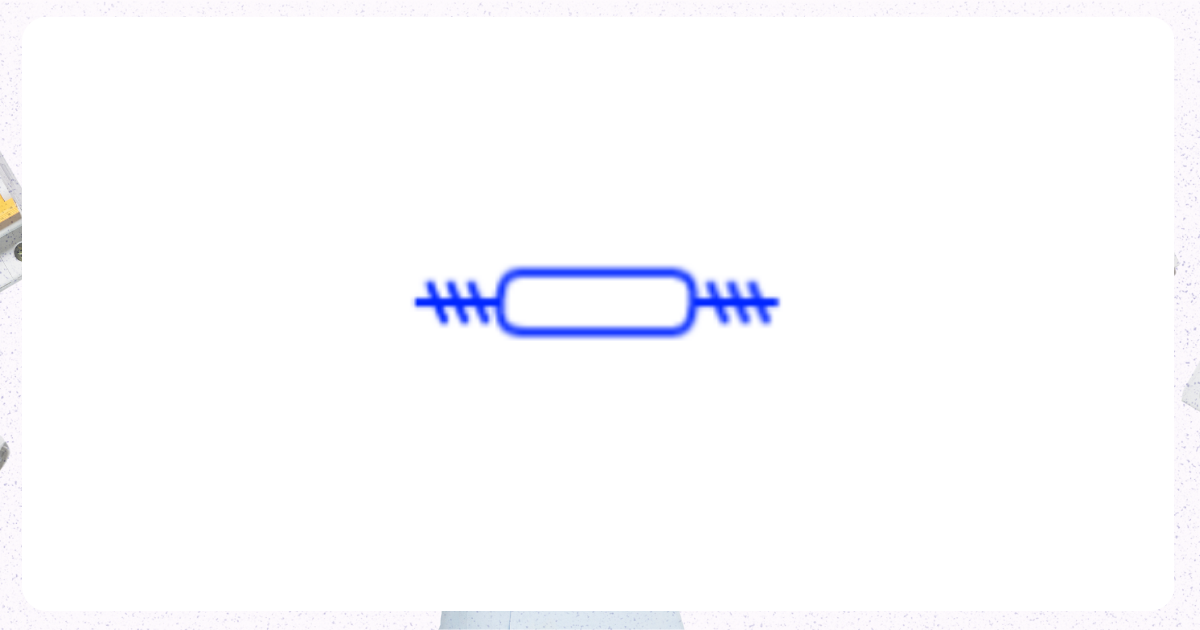
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
The purpose of this breaker is to safeguard three-phase electrical systems.
8. Isolator Circuit Breaker
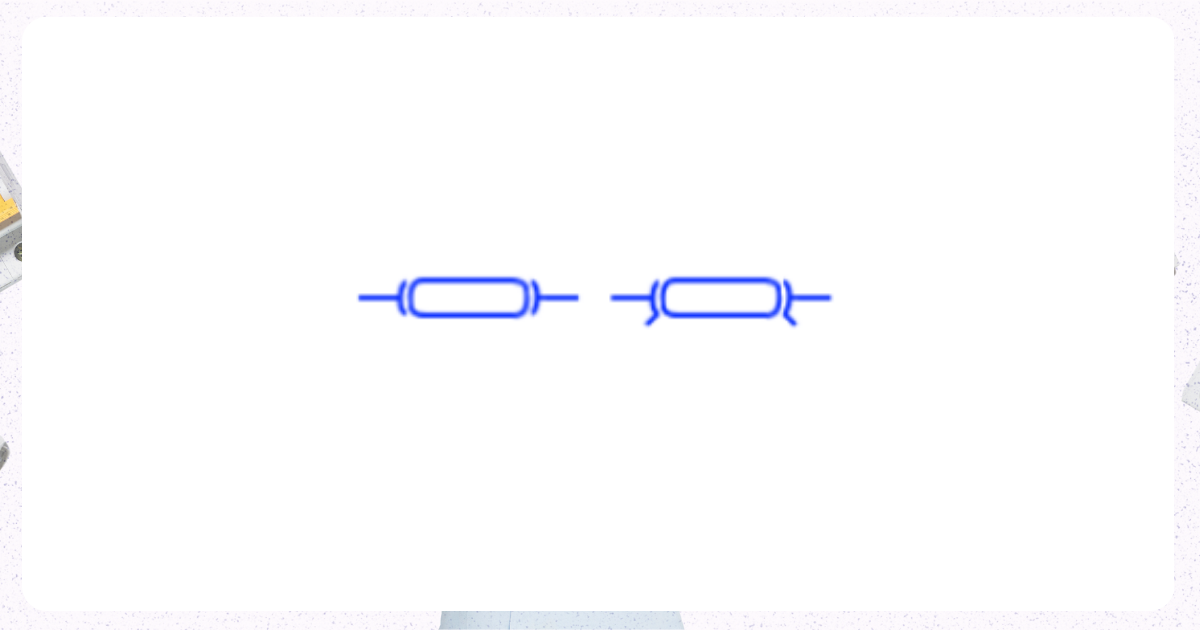

Image from Electrical Technology Organization
This is a switch that provides a means of disconnecting a circuit from its power source.
9. Cartridge Circuit Breaker
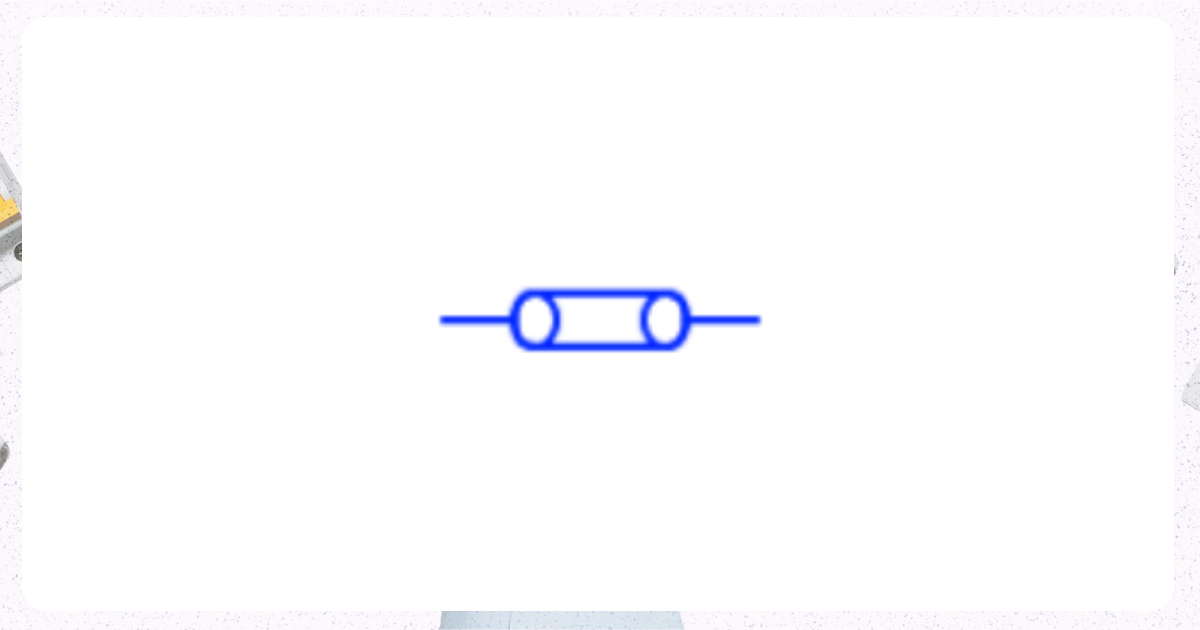
Image from Electrical Technology Organization
This is a type of circuit breaker that uses a cartridge containing the interrupting medium. The design of the cartridge causes it to blow when a fault arises, thereby interrupting the circuit.
How To Choose The Right Circuit Breaker
When selecting a circuit breaker, several factors must be considered to make sure that you have chosen the best type of safety device for your needs.
- Application and load requirements: Different applications have varying electrical loads, so the breaker must meet these needs.
- Voltage and current ratings: It’s crucial to choose a breaker that matches the system’s specific voltage and current.
- Safety features and certifications: Opt for breakers with appropriate safety certifications to ensure reliability.
Consulting with a qualified electrician is crucial for selecting the right circuit breaker, as they can provide expert advice tailored to individual needs.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance of circuit breakers are vital for their longevity and effectiveness.
- Best practices for installing circuit breakers:
- Ensure proper circuit design, considering the load and application.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines to guarantee compliance with safety standards.
- Maintenance tips for circuit breakers:
- Conduct regular inspections and testing to identify potential issues.
- Keep the area clean and dry to prevent moisture-related problems.
- Update or replace outdated breakers to maintain safety and efficiency.
Understanding Fuse and Circuit Breakers

Understanding circuit breakers and their symbols is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Familiarizing oneself with the different types and their applications can help you make informed decisions regarding the electrical infrastructure of your home. For optimal performance and safety, consider consulting professionals for installation and maintenance needs.
References:
ABB Electrification. (n.d.). Circuit Breaker Basics | ABB US. ABB Electrification. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://electrification.us.abb.com/circuit-breaker-basics
Electrical Technology. (n.d.). Fuse, Circuit Breaker and Protection Symbols. Electrical Technology. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2019/09/fuse-circuit-breaker-symbols.html
Electrical Technology. (n.d.). Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications. Electrical Technology. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2021/05/types-of-circuit-breakers.html
Idea Digital Content. (n.d.). Threaded Circuit Breakers and Enclosures. Idea Digital Content. https://www.ideadigitalcontent.com/files/11043/SPE_AEC_MC007_Threaded_Circuit_Breakers_and_Enclosures.pdf
Luminous Electric. (n.d.). How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker. Luminous Electric. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://www.lumelect.com/how-to-choose-the-right-circuit-breaker/
Nader Circuit Breaker. (2023, July 22). When do we use a 4 poles circuit breaker instead of a 3 poles circuit breaker? | Quisure Circuit Breaker. Nader Circuit Breaker. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://www.quisure-circuit-breaker.com/blog-technology-when-use-a-4-poles-circuit-breaker-instead-of-a-3-poles-circuit-breaker.html
RS Philippines. (n.d.). Cartridge Fuses | Glass Fuses | 13 Amp Fuses | RS. RS Philippines. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://ph.rs-online.com/web/c/fuses-circuit-breakers/fuses/cartridge-fuses/
Schneider Electric. (n.d.). Difference Between Isolators, RCCBs, and MCBs: A Comprehensive Guide. Schneider Electric. Retrieved November 4, 2024, from https://eshop.se.com/in/blog/post/difference-between-isolator-rccb-mcb.html